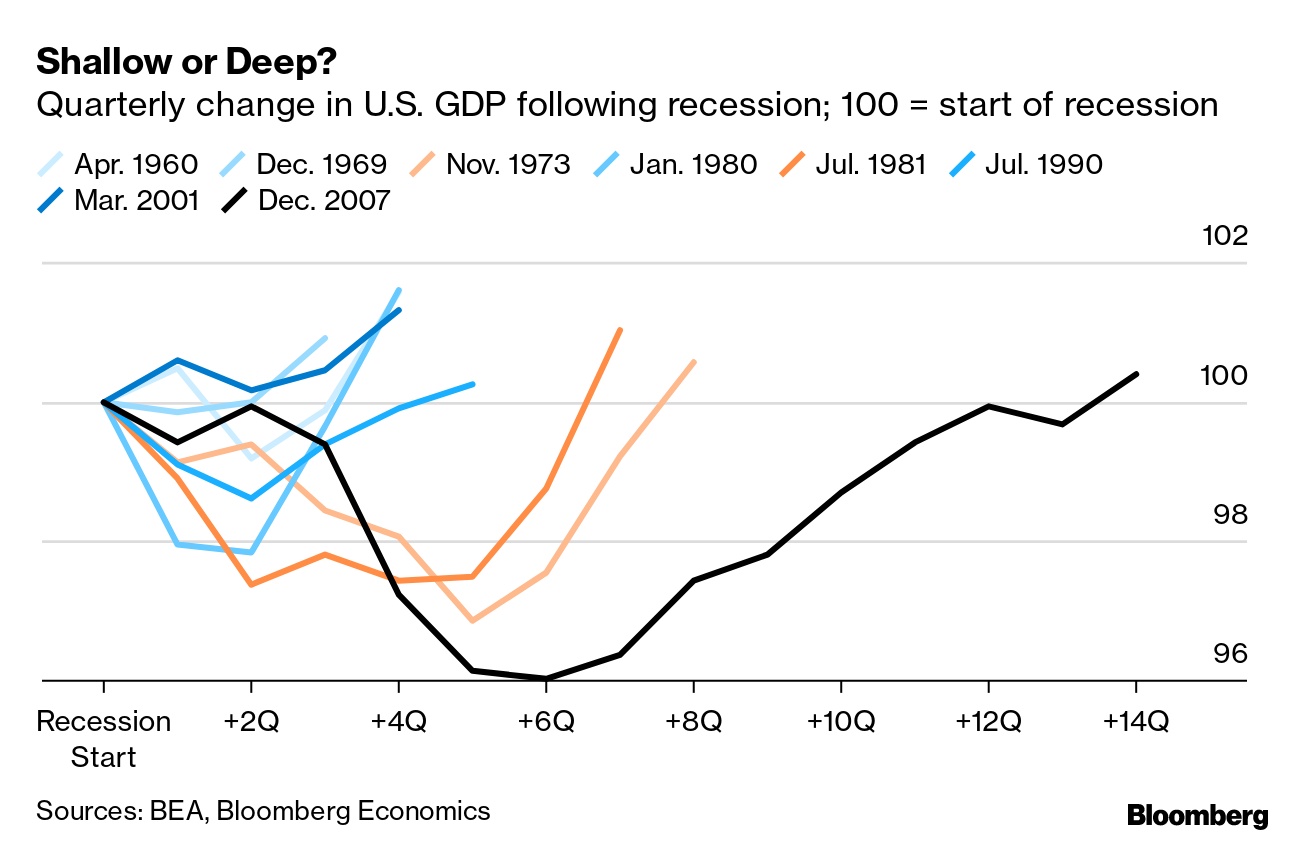
The U.S. economy is currently facing considerable challenges, with many experts warning that a recession could be on the horizon. This alarming sentiment is fueled by the ongoing trade war which has led to significant market fluctuations and influenced investor confidence. The Federal Reserve is grappling with the decision of whether to adjust interest rates in response to evolving economic indicators, including a declining consumer sentiment index reflecting waning economic confidence. Concerns over tariff impacts on the economy are amplifying worries that aggressive trade policies could catalyze downturns in growth and employment. As these dynamics unfold, it becomes crucial to understand the broader implications for the nation’s financial health in this precarious period.
In light of the recent economic turmoil, discussions surrounding a potential downturn in the American financial landscape are more pertinent than ever. The current landscape reveals an unsettling interplay between international trade disputes and domestic economic metrics, leading many to contemplate the implications of a possible economic slump. Observers note that the uncertainty stemming from rising tariffs and fluctuating market sentiments could lead to detrimental effects on both consumer behavior and investor confidence. Furthermore, as policymakers, especially within the Federal Reserve, navigate their options regarding interest rates, the overarching question remains: how will these factors collectively shape the trajectory of the U.S. economic landscape? Understanding the intricate connections between these elements is vital for anticipating future challenges and opportunities.
Impact of Trade War on the U.S. Economy
The ongoing trade war, particularly between the U.S. and major trading partners like China, Mexico, and Canada, has created a ripple effect that threatens to destabilize the U.S. economy. Tariffs imposed by these countries on American goods have not only impacted trade balances but have also led to increased costs for manufacturers and consumers alike. As businesses adjust to these new costs, consumer spending has the potential to decline, which could fuel a vicious cycle of reduced economic activity, ultimately pushing the economy closer to a recession.
Moreover, the uncertainty created by the trade war has dampened investor confidence, as reflected in the significant downturn in the stock market. Many investors are concerned about the long-term implications of persistent tariffs and retaliatory measures, leading to a cautious approach to investment. This lack of confidence is evident in the latest consumer sentiment index, which has hit its lowest mark since November 2022, indicating that Americans are becoming increasingly anxious about their economic futures.
Federal Reserve Interest Rates and Economic Outlook
The Federal Reserve is in a precarious position as it grapples with the implications of rising tariffs and the associated risks to economic stability. With the consumer sentiment index reflecting decreased economic confidence, the Fed may consider varying its interest rate policies to stimulate growth. Implementing interest rate cuts might provide a temporary fix to energize investment and consumer spending. However, cutting rates in the midst of rising inflation expectations poses a risk of overheating the economy, complicating the Fed’s decision-making process.
As the Fed weighs its options, the contrasting pressures of needing to support economic growth while controlling inflation create a challenging landscape. Analysts predict that maintaining stable interest rates may be the preferred path to prevent exacerbating current economic volatility. In these times of uncertainty, where trade tensions loom large, the Federal Reserve’s ability to foster economic resilience will be crucial in preventing a potential recession.
Understanding the Consumer Sentiment Index
The Consumer Sentiment Index (CSI) is a vital indicator that provides insight into the overall economic outlook from the consumers’ perspective. A fall in the CSI, as seen recently, signals growing concerns among the populace about financial stability, job security, and spending power. This deterioration often precedes decreased consumer spending, which accounts for a significant portion of the U.S. economy. As Americans hesitate to make large purchases or investments, businesses may face shrinking revenues, prompting layoffs and further contributing to economic slowdowns.
Moreover, a declining consumer sentiment can amplify the risks associated with potential recessionary conditions. When consumers feel less confident, their spending habits shift, and this can lead to increased savings rather than expenditure. Such behavior can negatively impact sectors reliant on discretionary spending, exacerbating challenges for the broader economy. Understanding these sentiments in conjunction with factors like the trade war and Federal Reserve policies will be essential in navigating the near-term economic landscape.
Tariff Impact on the Economy
Tariffs can have far-reaching effects on an economy, influencing everything from production costs to consumer prices. By imposing tariffs, the government aims to protect domestic industries; however, the unintended consequences often outweigh these benefits. Higher tariffs on imported goods lead to increased costs for manufacturers who rely on these inputs, ultimately resulting in higher prices for consumers. This dynamic can squeeze household budgets and reduce disposable income, thereby negatively impacting overall economic performance.
The tariff impact also extends to international relations and trade dynamics. As countries retaliate with their own tariffs, the resulting trade war can stifle economic growth, instigate job losses in affected industries, and generate broader economic insecurity. As businesses reassess their operations within this unstable environment, investment in growth and innovation may decline, potentially setting the stage for a recession if these trends persist.
Exploring Economic Confidence in Today’s Market
Economic confidence is a critical driver of growth and stability in any economy. In today’s market, the dip in economic confidence is alarming, particularly given the unstable political climate and international tension created by ongoing trade disputes. When consumers and businesses lack confidence, their spending and investment behaviors tend to reflect caution, which can consequently hinder economic expansion and innovation.
Recent reports suggest that as businesses adopt a ‘wait and see’ approach in response to fluctuating market conditions and government policy changes, economic momentum stalls. This reluctance can delay new projects and hiring plans, further exacerbating concerns of a potential recession. It is essential for market players to re-establish a sense of confidence, as a return to positive sentiment could significantly bolster economic performance and restore growth trajectories.
The Role of Risk Perception in Economic Decisions
Risk perception plays a pivotal role in economic decision-making, influencing both consumer behavior and investor sentiment. Heightened uncertainty surrounding tariffs and geopolitical events can lead to increased perceived risk, prompting individuals and businesses to tighten their belts. Such behavior not only dampens consumer spending but can also result in reduced capital investments, further stifling economic growth.
In an environment marked by unpredictability, stakeholders are likely to prioritize safety over risk, leading to a reluctance to engage in activities that could stimulate the economy. This increased perception of risk results in investments being postponed or shifted to safer assets, crippling innovation and growth in more volatile markets. Addressing these perceptions is critical for restoring confidence and reviving economic dynamism.
Forecasting a Future Shift in Economic Policies
As the U.S. government navigates turbulent economic waters, it is imperative to reassess its policy actions and determine a path forward that fosters stability and growth. The conflicting demands of controlling inflation while stimulating economic activity will require a delicate balancing act from policymakers and the Federal Reserve alike. There is a growing consensus that a recalibration of existing policies may be necessary to accommodate for the evolving economic landscape, particularly in light of trade tensions and fluctuating consumer sentiment.
Analysts suggest exploring alternative policy measures that can mitigate the adverse effects of tariffs while promoting investment and economic confidence could be vital moving forward. By fostering an environment conducive to growth, the government can help alleviate concerns of a looming recession and encourage a more robust economic outlook. This requires not only strategic economic planning but also effective communication to instill confidence across markets and communities.
The Consequences of Erratic Economic Policies
The erratic nature of recent economic policies, particularly those relating to tariffs and trade, has introduced a level of uncertainty that is detrimental to economic stability. Unpredictability in policy-making not only affects investor confidence but can also reverberate through consumer behavior, as individuals and businesses become wary of how these shifts may impact their financial activities. As a consequence, businesses may delay investments or expansion plans while consumers may choose to reduce spending, fueling economic stagnation.
Moreover, a lack of coherent strategy can lead to inefficiencies within the economy, as resources are misallocated and businesses adapt to survive rather than thrive. This inefficiency creates a more fragile economic structure, making it susceptible to shocks that could lead to severe downturns. A concerted effort to establish consistent and predictable policies is essential for creating an environment where businesses can confidently invest and consumers can feel secure in their financial decisions.
Strategies to Mitigate Recession Risk
Given the potential risks of recession looming on the horizon due to current economic conditions, it is crucial for policymakers to devise strategies to mitigate these risks effectively. This could range from encouraging fiscal measures aimed at stimulating economic activity to creating safety nets for industries adversely affected by tariffs. Drawing lessons from past economic downturns, proactive measures can help cushion the impacts of a recession and lay groundwork for a more resilient economy.
Furthermore, engaging with industry leaders to understand their challenges and foster stronger collaborations can play a pivotal role in devising targeted strategies. By prioritizing job creation and supporting sectors that drive growth, policymakers can help build consumer confidence and promote economic stability. A multifaceted approach that balances short-term relief with long-term economic improvements will be essential in preventing a recession and sustaining growth in the U.S. economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the potential effects of a U.S. economy recession on consumer sentiment?
A U.S. economy recession can significantly impact consumer sentiment, often leading to decreased confidence among consumers. As the economy contracts, people may feel uncertain about their financial stability, resulting in lower spending and investment. Reports from the University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index indicate that during recessionary periods, economic confidence typically drops, reflecting worries about job security and overall economic conditions.
How does the trade war affect the likelihood of a U.S. economy recession?
The trade war, characterized by tariffs imposed on imports, can exacerbate the risk of a U.S. economy recession. Tariffs can lead to increased costs for consumers and businesses, disrupt supply chains, and create uncertainties in the marketplace. This regulatory environment often contributes to a decline in economic growth, potentially propelling the nation towards recession.
What role do Federal Reserve interest rates play during a U.S. economy recession?
During a U.S. economy recession, the Federal Reserve may adjust interest rates to stimulate economic growth. Lowering Federal Reserve interest rates can encourage borrowing and spending, which is crucial during economic downturns. Conversely, if inflation remains high, the Fed may choose to keep rates steady, weighing the benefits of supporting economic recovery against the risks of fostering further inflation.
How do tariffs impact the economy during a U.S. economy recession?
Tariffs can have a detrimental impact on the economy during a U.S. economy recession by increasing costs for consumers and businesses. This leads to higher prices and reduced overall demand. Additionally, tariffs can cause retaliatory measures from trading partners, further straining international trade relations and potentially deepening the economic downturn.
What indicators suggest the U.S. economy is headed for a recession?
Several indicators suggest the U.S. economy might be headed for a recession, including a declining consumer sentiment index, rising unemployment rates, and significant fluctuations in the stock market. Additionally, macroeconomic factors like trade war effects and shifts in Federal Reserve interest rates can further influence perceptions of economic stability and confidence.
How can consumer sentiment index predict a U.S. economy recession?
The consumer sentiment index is a valuable predictor of a U.S. economy recession as it reflects the overall confidence of consumers about their financial situation and the economy’s future. A falling index points towards increasing pessimism and may foreshadow reduced consumer spending, which is crucial for economic growth and can lead to recession if sustained.
What are the risks of a prolonged trade war on the U.S. economy?
A prolonged trade war poses significant risks to the U.S. economy, including potential recession. It can disrupt trade relations, lead to increased tariffs, and ultimately harm domestic industries. The resulting volatility can diminish economic confidence among consumers and investors, compounding risks and uncertainties in the financial market.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Current Market Conditions | U.S. markets have faced significant declines due to tariff increases from China, Mexico, and Canada. |
| Consumer Sentiment | The University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index has plummeted to its lowest since November 2022. |
| Impact of Tariffs | Economist Jeffrey Frankel states tariffs are generally harmful, citing few instances where they may be justified. |
| Market Selloff and Economic Stability | Treasury Secretary claims the market decline is a normal correction, though experts dispute this. |
| Risk Factors for Recession | Potential risks include trade wars, stock market crashes, cuts in government spending, and increased perception of economic risk. |
| Federal Reserve’s Dilemma | The Fed faces a conflict between cutting rates to support jobs and maintaining rates to control inflation. |
Summary
The U.S. economy recession is becoming a genuine concern as increased tariffs and trade disputes create instability in the market. With consumer confidence dropping to historic lows, the potential for a recession looms larger than before. Economic experts highlight various risk factors, including trade wars and market volatility, which could lead to reduced employment and income. The Federal Reserve faces a challenging decision on interest rates as they navigate these turbulent times, indicating that the overarching economic climate could indicate a downturn ahead. In this context, careful monitoring of economic signals is crucial to prepare for any impending recession.